Dynamic Time Warping
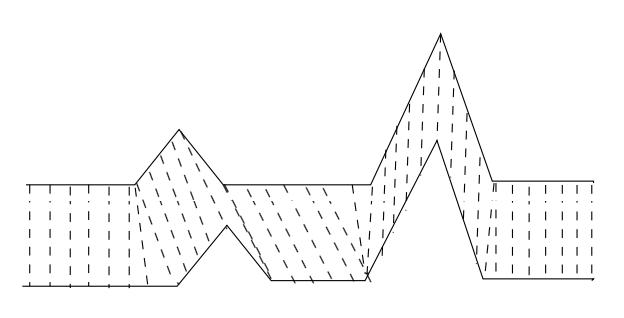
Dynamic time warping (DTW) is an algorithm for measuring similarity between two temporal sequences, which may vary in speed. For instance, similarities in walking could be detected using DTW, even if one person was walking faster than the other, or if there were accelerations and decelerations during the course of an observation
DTW is a method that calculates an optimal match between two given sequences (e.g. time series) with certain restriction and rules:
- Every index from the first sequence must be matched with one or more indices from the other sequence, and vice versa
- The first index from the first sequence must be matched with the first index from the other sequence (but it does not have to be its only match)
- The last index from the first sequence must be matched with the last index from the other sequence (but it does not have to be its only match)
- The mapping of the indices from the first sequence to indices from the other sequence must be monotonically increasing, and vice versa, i.e. if $j > i$ are indices from the first seuence, then there must not be two indices $l > k$ in the other sequence, such that index $i$ is matched with $l$ and $j$ is matched with $k$.
We can plot each match between the sequences $1 : M$ and $1 : N$ as a path in a $M \times N$ matrix from $(1, 1)$ to $(M, N)$ such that each step is one of $(0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1)$.
The optimal match is denoted by the match that satisfies all the restrictions and the rules and that has the minimal cost, where the cost is computed as the sum of absolute differences, for each matched pair of indices, between their values.
Implementation
1type Pair struct {
2 x int
3 y int
4}
5
6type distance func(int, int) int
7
8func DTWDistance(s, t []int, dist distance) []Pair {
9 matrix := [][]int{}
10 n, m := len(s), len(t)
11 for i := 0; i < n+1; i++ {
12 row := []int{}
13 for j := 0; j < m+1; j++ {
14 row = append(row, int(math.Inf(1)))
15 }
16 matrix = append(matrix, row)
17 }
18 matrix[0][0] = 0
19
20 for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
21 for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
22 cost := dist(s[i], t[j])
23 matrix[i+1][j+1] = cost + min(matrix[i][j+1], matrix[i+1][j], matrix[i][j])
24 }
25 }
26 path := []Pair{{0, 0}}
27 for i, j := 1, 1; i < n && j < m; {
28 costs := map[int]Pair{
29 matrix[i][j+1]: {i, j + 1},
30 matrix[i+1][j]: {i + 1, j},
31 matrix[i][j]: {i, j},
32 }
33 var pair Pair
34 minVal := int(math.Inf(1))
35 for k, v := range costs {
36 if k < minVal {
37 minVal = k
38 pair = v
39 }
40 }
41 path = append(path, pair)
42 }
43 return path
44}References
#machine learning #time series #algorithm #programming #statistics #forecasting